
Professional Weld Stud Solutions and Industrial Applications
Weld studs are engineered fasteners that are welded directly onto a metal substrate to create a permanent fixing point without drilling through the parent material. This supports one sided assembly where the reverse face must stay clean, sealed or cosmetically finished such as cabinets, panels and enclosures.
In production environments stud welding can increase throughput by reducing marking out, drilling, deburring and rework. For thin sheet applications capacitor discharge (CD) welding is commonly used because the weld cycle is extremely short with low heat input which helps reduce distortion and surface marking. For heavier sections drawn arc stud welding is typically selected to provide high strength joints on structural components and thick fabrications.
Process selection
CD welding suits thin gauge sheet metal and coated panels where minimal heat input is critical. Drawn arc welding suits thicker steelwork where higher weld penetration and load capacity are required.
Typical technical checks
Common checks include visual inspection of weld fillet, bend testing where applicable, torque checks for threaded studs and verification of dimensions against ISO form.
Professional Weld Stud Components
Precision weld studs engineered for reliable permanent fastening across manufacturing, fabrication and building services.
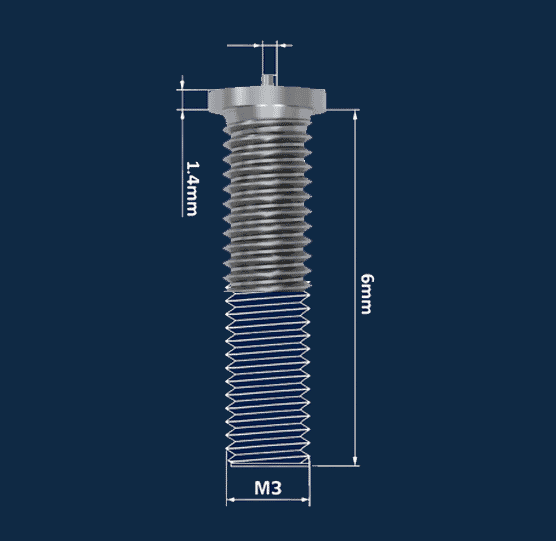
Male Threaded Weld Studs - ISO 13918 Type PT
External thread studs for fast nut on assembly. Common for mounting brackets, clamps, cable management and equipment supports where a repeatable torque tightened joint is required.
- ISO 13918 Type PT form for consistent geometry
- Practical for fast assembly and maintenance access
- Used on steel panels, frames and enclosures
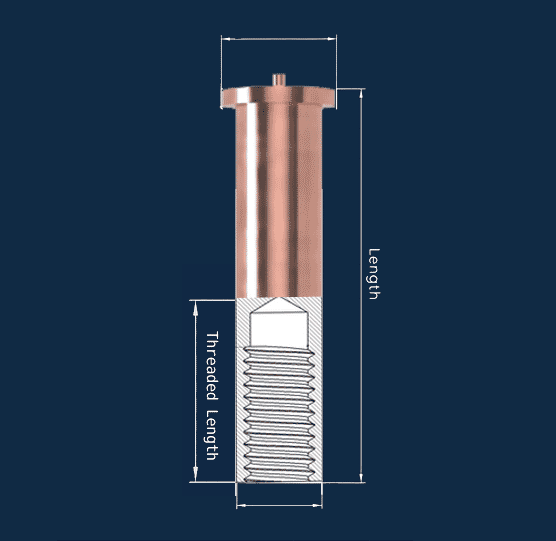
Female Threaded Weld Studs - ISO 13918 Type IT
Internal thread studs provide a protected thread for bolts which supports flush finishes and reduces snag risk in tight assemblies such as electrical cabinets, kiosks and vehicle interiors.
- ISO 13918 Type IT form for internal thread fixing
- Supports removable bolted assemblies
- Useful where external threads are not preferred
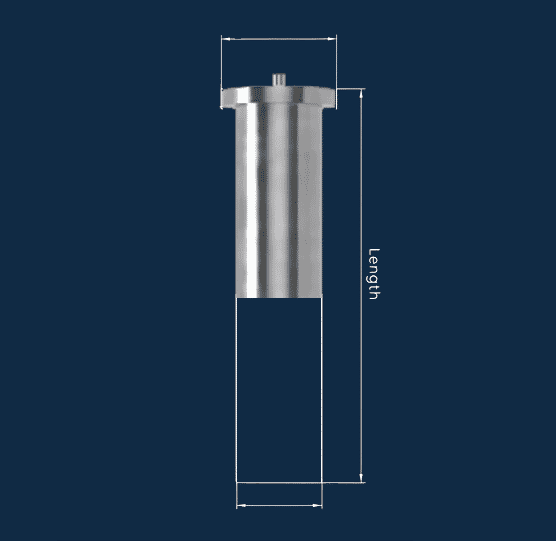
Unthreaded Weld Studs - ISO 13918 Type UT
Plain shank studs for location, alignment and clip on components. Often used where a pin is required for insulation retainers, spacers, spring clips and custom secondary operations.
- ISO 13918 Type UT form for plain stud geometry
- Supports press on parts, clips and retainers
- Ideal where machining or custom ends are required
Industry Applications
Weld studs support rapid, repeatable assembly in high volume production and durable fixing points in site environments. Below are practical application examples by sector.
- Electrical enclosures: mounting plates, DIN rail brackets, earthing straps
- HVAC: supports, insulation retainers, brackets on ducting and plant equipment
- Automotive: heat shields, trim brackets, cable routing and lightweight assemblies
- Marine: interior panels and furniture where through holes are not desired
Technical Use Cases Across UK Industry
Electrical, control panels and enclosures
Studs are used to mount internal backplates, hinge supports, cable trunking and earthing points. Female threaded studs help achieve a flush internal profile for removable assemblies. CD welding is often selected on thin sheet to help reduce distortion during enclosure manufacture.
HVAC, building services and plant rooms
Weld studs provide mounting points for brackets, hangers and insulation retainers on ducting and equipment housings. Male threaded studs support quick nut on installation for service access and component replacement.
Automotive, rail and vehicle conversion
Studs support repeatable assembly for brackets, heat shields and component mounting where access is limited to one side. The welded joint reduces loose parts handling compared with nuts and bolts on both sides.
Fabrication, machinery guards and sheet metal
Studs are used for mounting panels, covers and guard fixings where a clean finish is required. Unthreaded studs can be used as locating pins for jigs, fixtures and clip on assemblies to reduce build time.
Marine interiors and boatbuilding
Studs attach to panels rather than passing through them which helps preserve watertight integrity where through holes are not suitable. They also support cleaner finished surfaces on visible joinery and interior structures.
Renewables, cabinets and outdoor equipment
Studs are used in mounting systems for inverter cabinets, battery enclosures and external housings. Material choice becomes important for corrosion resistance and stainless steel options may be selected for harsh environments.
Technical Industry Applications for Weld Studs
Weld studs provide a permanent fixing point on one side of the parent material which removes the need for through holes. This supports faster assembly, improved sealing and cleaner finished surfaces on panels, enclosures and fabricated frames. Capacitor discharge stud welding is commonly used on thin sheet metal to minimise heat input while drawn arc stud welding is used on thicker steel sections where higher load capacity is required.
Electrical enclosures and control panels
Weld studs are widely used for mounting internal backplates, DIN rail systems, earthing straps and cable management hardware. Female threaded studs allow removable bolted connections while maintaining a flush internal profile which reduces snag risk around wiring looms and trunking. CD welding is often selected for thin sheet to help reduce distortion during enclosure manufacture.
HVAC and building services
In HVAC applications weld studs provide reliable fixing points for brackets, hangers and insulation retainers on ducting and equipment housings. Male threaded studs support rapid nut on installation which simplifies servicing and component replacement in plant rooms. Unthreaded studs are also used as pins for clips and retainers on lightweight assemblies.
Automotive, rail and vehicle manufacturing
Used extensively for repeatable assembly of heat shields, trim brackets, cable routing clips and lightweight sub assemblies. Stud welding reduces loose component handling and supports consistent build quality where access is limited to one side of the assembly. This can improve takt time in production cells and reduce rework caused by misalignment.
Fabrication and sheet metal assemblies
Weld studs are used on guards, panels and covers where the reverse face must remain clear for safety or appearance. Unthreaded studs can be used as locating pins for jigs and fixtures to improve alignment accuracy and reduce build time. Male threaded studs support quick bracket installation on frames, bases and equipment housings.
Marine interiors and boatbuilding
In marine interiors weld studs attach to panels rather than passing through them which helps preserve watertight integrity. This makes them suitable for furniture, interior panels and structural joinery where exposed fasteners are undesirable. Studs also support cleaner finished surfaces for visible fit out components.
Outdoor enclosures and renewable equipment
Weld studs are used in mounting systems for inverter cabinets, battery enclosures and external housings where vibration resistance and service access matter. Material selection becomes important for corrosion performance and stainless steel options may be selected for harsher environments.
Which Materials are Suitable for Weld Stud Applications?
Material selection depends on the stud welding method, parent material thickness, coatings and corrosion requirements. Copper coated steel studs are commonly specified on steel fabrications. Stainless steel studs are often used where corrosion resistance is required. Aluminium studs are typically matched to aluminium parent materials with suitable preparation and process control.
| Parent Material | Copper Coated Steel | Stainless Steel | Aluminium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Carbon Steel | Good | Good | Process dependent |
| Steel up to 0.6% Carbon | Fair | Good | Process dependent |
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | Good | Good | Process dependent |
| Zinc Coated Steel | Fair | Fair | Process dependent |
| Hot Rolled Structural Steel | Fair | Fair | Process dependent |
| Aluminium | Process dependent | Process dependent | Good |
| Brass (Lead Free) | Process dependent | Process dependent | Process dependent |
| Copper (Lead Free) | Process dependent | Process dependent | Process dependent |
Notes: coatings such as zinc can influence weld quality and fume control requirements. Surface cleanliness, contact, grounding and parameter control all affect consistency.
Practical Process Guidance
Surface preparation and fit up
Parent material should be free from paint, heavy oxide, grease and surface contamination in the weld zone. Correct gun alignment and full contact at the weld location helps achieve consistent fusion and reduces misfires.
Quality checks for production
Typical production checks include visual weld assessment, periodic bend tests where applicable, thread gauge checks and torque verification for threaded studs. Recording parameters supports traceability for repeat builds.
When CD welding is a good fit
CD welding is often chosen for thin sheet where low heat input is required to help reduce distortion. It is commonly used on enclosures, ductwork, kiosks, cabinets and light fabrication assemblies.
When drawn arc welding is a good fit
Drawn arc welding is typically used on thicker steelwork where higher load capacity and deeper fusion are required. It is often selected for heavy fabrication, structural brackets and equipment frames.
Shop Weld Studs for Production and Site Work
View threaded and unthreaded options for reliable one sided fastening on panels, fabrications and structural components.
Match the stud type, material and welding process to the parent material and service environment. For projects that require help selecting the right weld stud form and size, Vital Parts can support with technical product guidance







Leave a comment